A Vision for Sri Lanka’s Agricultural Future
Agriculture has long been the backbone of Sri Lanka’s economy, sustaining millions of livelihoods across rural communities. Yet, in a rapidly globalizing world, the challenge is not just to produce—but to compete, innovate, and export sustainably.
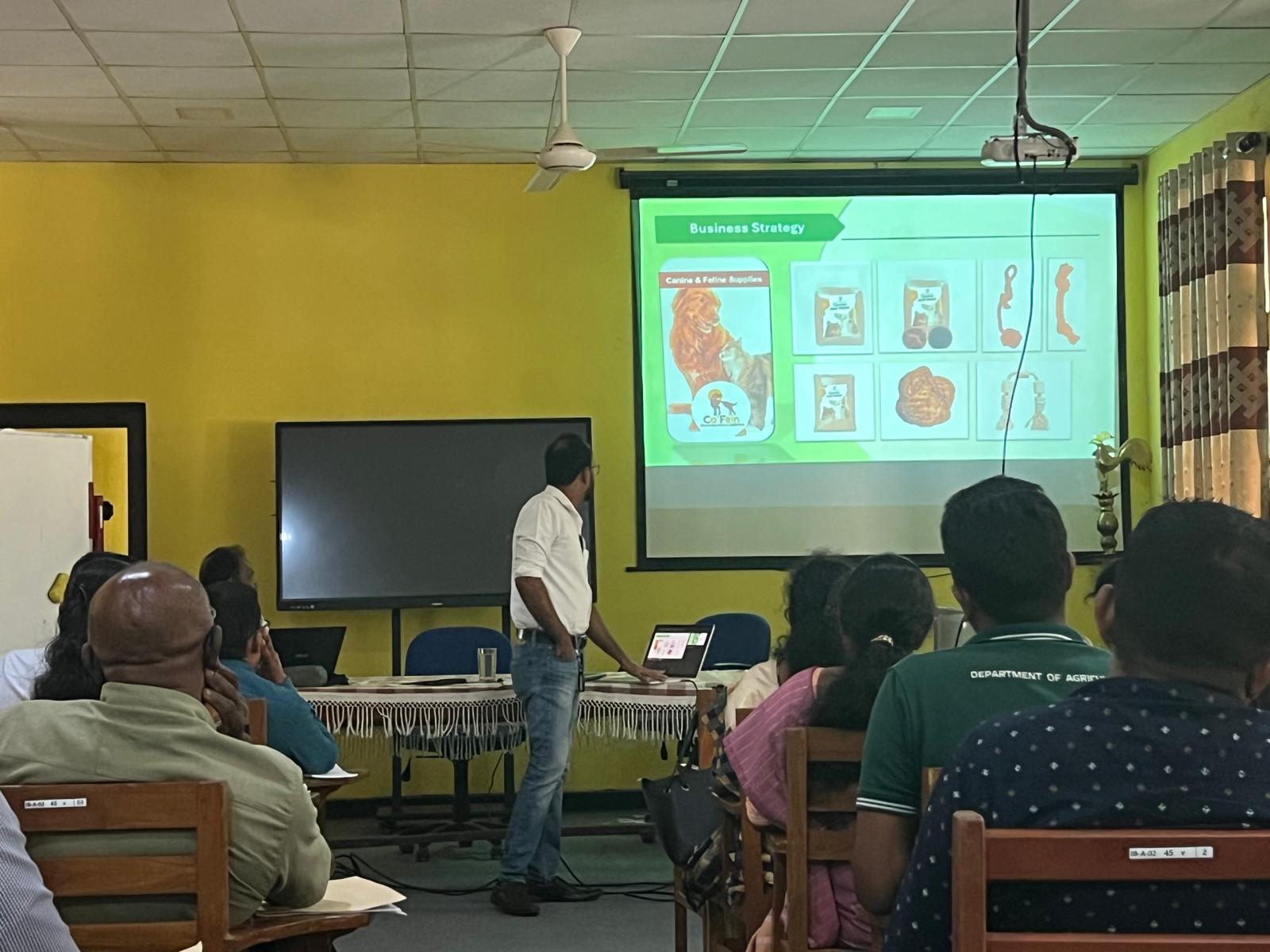
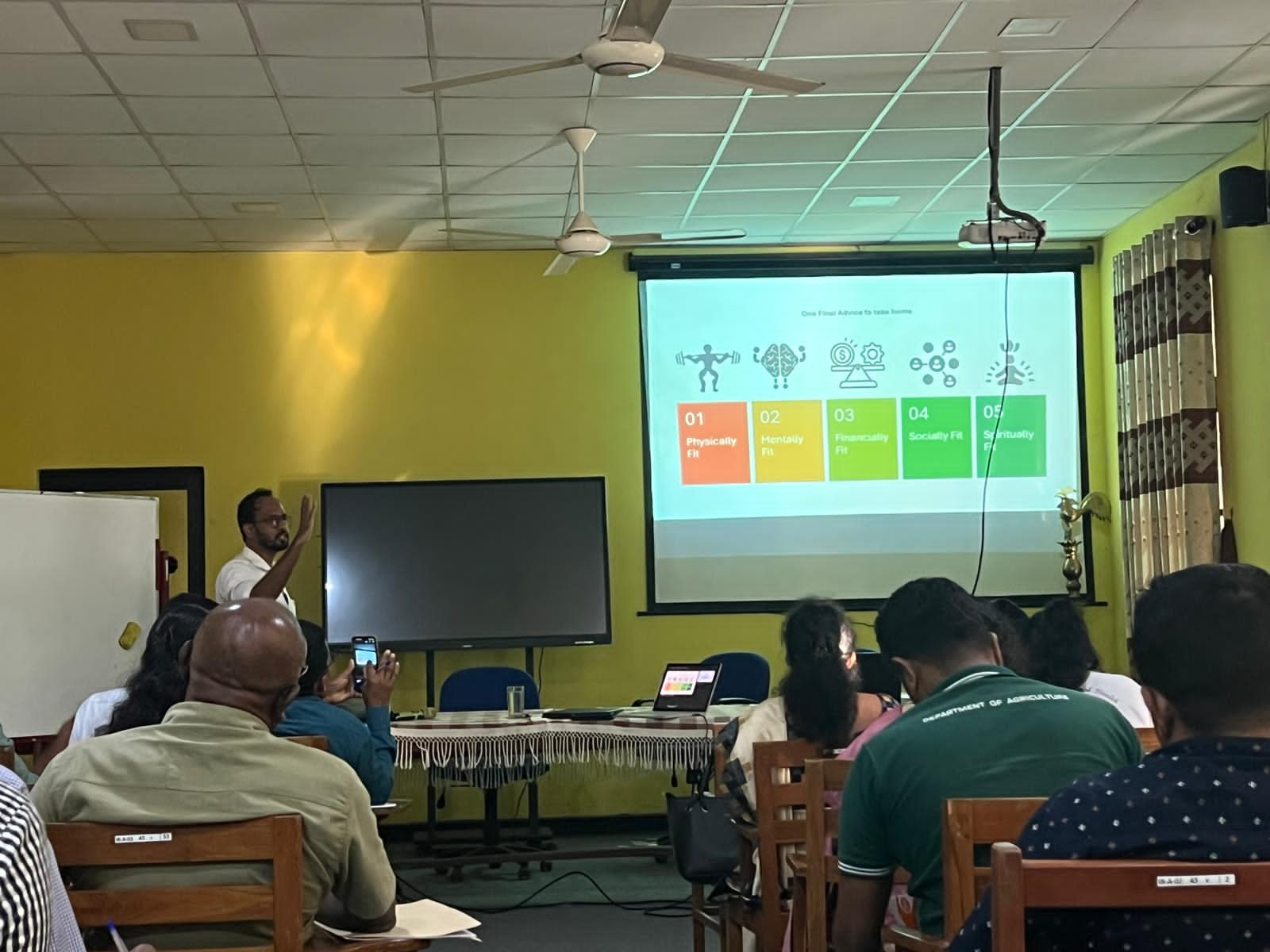
At the Regional Agriculture Instructors Event in Belihuloya, Mr. Namal Jayasekara, CEO of Green Space International and Green Space LaunchLab (Pvt) Ltd, shared his powerful insights on transforming Sri Lanka’s agricultural ecosystem to meet global market demands.
His message was clear: empowering farmers requires more than training—it demands a complete rethinking of agricultural business models, rooted in cluster development, cooperative structures, and innovation-driven sustainability.
Sri Lanka’s Agricultural Landscape: Opportunities and Challenges
Despite Sri Lanka’s fertile land and rich biodiversity, many farmers struggle to access profitable markets. Fragmented supply chains, limited technology adoption, and inconsistent quality standards have long hindered the nation’s agricultural competitiveness.
However, global market trends are shifting rapidly toward:
- Ethical sourcing and sustainability
- Organic and traceable products
- Community-driven agricultural clusters
These trends open a window of opportunity for Sri Lanka—if farmers can align production, quality, and branding with global standards.
Green Space International’s Commitment to Agricultural Transformation
About the Company
Green Space International (Pvt) Ltd and its innovation arm Green Space LaunchLab are dedicated to developing sustainable industries that merge community empowerment with global trade.
From eco-friendly product exports to agricultural innovation, the company focuses on creating value chains that benefit both producers and the environment.
Their mission extends beyond business success—to enable inclusive rural growth, where farmers become not just suppliers, but stakeholders in international trade.
Insights from the Regional Agriculture Instructors Event
During the Belihuloya event, Mr. Jayasekara outlined a holistic strategy for Empowering Sri Lankan Farmers for Global Markets, built around four key pillars:
- Strategic Farmer Cluster Development
- Cooperative Export Organizations
- Comprehensive Support Ecosystems
- Business Development and Sustainable Practices
Each of these components forms part of a unified roadmap designed to transform traditional farming into a globally competitive agricultural system.
1. Strategic Farmer Cluster Development
From Isolation to Collaboration
One of the biggest challenges faced by Sri Lankan farmers is scale. Many operate independently, producing small quantities that limit bargaining power and export potential.
Green Space proposes a cluster development model—organizing farmers into collaborative groups based on crop type, region, and market potential.
Benefits of the Cluster Model
- Economies of Scale: Collective purchasing and selling improve margins.
- Standardization: Shared knowledge ensures product quality and consistency.
- Market Access: Larger volumes attract export buyers.
- Innovation Sharing: Clusters encourage adoption of new farming techniques and technologies.
“When farmers unite under a shared vision,” said Mr. Jayasekara, “they move from surviving individually to thriving collectively.”
2. Cooperative Export Organizations
Empowering Farmers Through Ownership
Export success isn’t just about production—it’s about market access and control.
Green Space advocates forming cooperative export organizations that enable farmers to take ownership of their export journey.
These cooperatives serve as collective trading entities, allowing farmers to:
- Negotiate better prices.
- Manage logistics and certifications.
- Retain profits within local communities.
- Ensure fair trade and transparency.
The Green Space Approach
Green Space LaunchLab provides technical and business support to help these cooperatives connect with:
- International buyers.
- Certification bodies for organic and sustainable produce.
- Export facilitation networks such as the Sri Lanka Export Development Board (EDB).
This structure ensures that farmers don’t remain at the mercy of intermediaries—they become empowered exporters themselves.
3. Comprehensive Support Ecosystems
Beyond Farming: Creating a 360° Support Network
Sustainability in agriculture doesn’t stop at production. Green Space’s approach is to build comprehensive ecosystems that integrate all aspects of value creation—from seed to shipment.
This involves:
- Access to finance through partnerships with banks and microfinance institutions.
- Capacity building via training programs on international standards and best practices.
- Technology adoption—introducing IoT, smart irrigation, and precision agriculture tools.
- Data-driven decision-making through digital platforms for monitoring yields and soil health.
Technology as a Game-Changer
By integrating modern technology into agriculture, farmers can improve efficiency, predictability, and profitability.
Green Space LaunchLab’s initiatives are helping farmers:
- Use data to reduce waste.
- Forecast weather and crop cycles.
- Manage resources sustainably for long-term yield stability.
4. Business Development and Sustainable Practices
Turning Farmers into Entrepreneurs
The transition from farmer to agripreneur is at the heart of Green Space’s model. Farmers are encouraged to see their work as part of a value-driven enterprise—where quality, branding, and innovation play key roles.
Training sessions and mentorship programs help farmers understand:
- Market trends and consumer behavior.
- Export documentation and compliance.
- Brand storytelling and value addition.
Sustainability as a Competitive Advantage
Green Space promotes sustainable farming practices, including:
- Organic fertilizer usage.
- Renewable energy for processing.
- Eco-friendly packaging for export goods.
Such practices not only reduce environmental impact but also enhance brand reputation and export value in sustainability-focused markets like the EU and Japan.
Building a Strong Agricultural Value Chain
A solid value chain connects all players—farmers, processors, exporters, and consumers—through transparent, efficient systems.
Green Space’s model focuses on:
- Traceability: Ensuring every product’s journey from farm to shelf is documented.
- Quality Control: Maintaining international certification standards.
- Brand Identity: Promoting Sri Lankan produce as a mark of excellence.
By creating interconnected value chains, Green Space ensures that farmers don’t just produce—they participate in the global economy.
Empowering Farmers Through Green Space LaunchLab
Innovation for Impact
Green Space LaunchLab Pvt Ltd acts as the innovation accelerator for the company’s agricultural projects.
It develops pilot programs that:
- Test new technologies.
- Support startups in agritech.
- Facilitate collaboration between researchers, exporters, and rural entrepreneurs.
A Platform for Farmer Entrepreneurship
Through LaunchLab, farmers gain exposure to modern business tools, digital solutions, and mentorship, helping them transition into export-oriented microenterprises.
Sustainability and Social Responsibility
Green Space’s agricultural model aligns with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly:
- SDG 1: No Poverty
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- SDG 13: Climate Action
By fostering sustainable agriculture, Green Space contributes to both local empowerment and global environmental responsibility.
The Role of Institutions and Collaboration
To scale this transformation, Green Space emphasizes the importance of public-private partnerships (PPPs).
Collaboration with:
- The Department of Agriculture
- Export Development Board (EDB)
- Financial institutions and universities
is essential for providing the infrastructure, research, and policy support needed to make Sri Lankan agriculture globally competitive.
Global Opportunities for Sri Lankan Farmers
With rising international demand for:
- Organic spices
- Coconut-based products
- Tropical fruits
- Sustainable packaging materials
Sri Lankan farmers have the opportunity to access high-value export markets.
Green Space’s initiatives prepare them to meet global standards in quality, sustainability, and supply reliability.
Challenges and Path Forward
Key Challenges
- Limited access to export financing.
- Lack of standardized production systems.
- Inadequate marketing and branding.
Proposed Solutions
- Establishing regional export facilitation centers.
- Offering financial literacy programs for farmers.
- Developing a national brand for “Sustainably Grown in Sri Lanka” produce.
Green Space’s ongoing partnerships aim to address these gaps through targeted programs and policy advocacy.
A New Era for Sri Lankan Agriculture
The insights shared by Mr. Namal Jayasekara at the Belihuloya Regional Agriculture Instructors event represent more than a speech—they signify a national call to action.
Through Empowering Sri Lankan Farmers for Global Markets, Green Space International and Green Space LaunchLab Pvt Ltd are leading a transformative movement—one that connects local talent to global opportunities, builds sustainable communities, and redefines Sri Lanka’s role in the global agricultural economy.
This is not just about exports—it’s about creating a future where every Sri Lankan farmer grows, competes, and thrives on the world stage.